Dimorphic fungi: Difference between revisions
From IDWiki
Content deleted Content added
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
!Organism |
!Organism |
||
| Line 12: | Line 5: | ||
!Treatment |
!Treatment |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Blastomyces |
|[[Blastomyces]] |
||
|eastern US and Canada, with some reported in Africa |
|eastern US and Canada, with some reported in Africa |
||
|pulmonary infection, verrucous skin lesions, osteomyelitis, CNS infection |
|pulmonary infection, verrucous skin lesions, osteomyelitis, CNS infection |
||
|[[itraconazole]] (with [[amphotericin B]] induction if severe) |
|[[itraconazole]] (with [[amphotericin B]] induction if severe) |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Coccidioides |
|[[Coccidioides]] |
||
|southwestern US and parts of South and Central America |
|southwestern US and parts of South and Central America |
||
|pulmonary infection, verrucous skin lesions, osteomyelitis, CNS infection |
|pulmonary infection, verrucous skin lesions, osteomyelitis, CNS infection |
||
|[[fluconazole]] (with [[amphotericin B]] and [[flucytosine]] induction if severe) |
|[[fluconazole]] (with [[amphotericin B]] and [[flucytosine]] induction if severe) |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[ |
|[[Histoplasma capsulatum]] |
||
|worldwide, including eastern North America, Central and South America, sub-Saharan Africa, and parts of Southeast Asia |
|worldwide, including eastern North America, Central and South America, sub-Saharan Africa, and parts of Southeast Asia |
||
|pulmonary infection, CNS infection |
|pulmonary infection, CNS infection |
||
| Line 42: | Line 35: | ||
|[[amphotericin B]] induction followed by [[itraconazole]] |
|[[amphotericin B]] induction followed by [[itraconazole]] |
||
|} |
|} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
*Includes the following genera and species: |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
===Epidemiology=== |
===Epidemiology=== |
||
| Line 59: | Line 58: | ||
[[File:Histoplasmosis_map.png|Histoplasmosis|alt=|thumb|300x300px]] |
[[File:Histoplasmosis_map.png|Histoplasmosis|alt=|thumb|300x300px]] |
||
* |
*High-endemic areas include Ohio and Mississippi river valley systems, but also in Central and South America |
||
** |
**However, 12-20% of cases in US occur outside of endemic areas |
||
** |
**In Canada, mostly along St. Lawrence seaway and Great Lakes drainage |
||
* |
*More recently, cases have been diagnosed in Alberta and Saskatchewan |
||
* |
*Also found in Asia and Africa, throughout, with var. duboisii in West Africa (mostly skin and soft tissue disease) |
||
* |
*Associated with soil contaminated by bird or bat guano |
||
====Coccidiomycosis==== |
====Coccidiomycosis==== |
||
| Line 70: | Line 69: | ||
[[File:Coccidiomycosis_map.png|Coccidiomycosis|alt=|thumb|300x300px]] |
[[File:Coccidiomycosis_map.png|Coccidiomycosis|alt=|thumb|300x300px]] |
||
* |
*More common in southwestern US, especially California and Arizona (but up to Washington state), as well as parts of South and Central America |
||
** |
**Concentrated heavily in San Joaquin Valley in California |
||
* |
*Present in soil |
||
* |
*High-risk activities: construction, military maneuvers, earthquakes/landslides, armadillo hunting, prisoners from other parts of the US that are incarcerated in California |
||
====Blastomycosis==== |
====Blastomycosis==== |
||
| Line 79: | Line 78: | ||
[[File:Blastomycosis_map.png|Blastomycosis|alt=|thumb|300x300px]] |
[[File:Blastomycosis_map.png|Blastomycosis|alt=|thumb|300x300px]] |
||
* |
*Found mostly in eastern North America |
||
** |
**In Canada, found in northwestern Ontario, Quebec, Manitoba, and Saskatchewan |
||
*** |
***Kenora is the hotspot in Canada |
||
* |
*More common in wooded areas, damp soil, and near waterways |
||
* |
*High-risk activities include excavation and construction |
||
==== |
====Emergomycosis==== |
||
* |
*Different species found worldwide, including [[Emergomyces canadensis]] in Saskatchewan, Colorado, and New Mexico |
||
* |
*More common in HIV patients or other immunocompromised |
||
== |
==Clinical Manifestations== |
||
=== |
===Histoplasmosis=== |
||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
! |
! |
||
| Line 115: | Line 114: | ||
|} |
|} |
||
=== |
===Blastomycosis=== |
||
* |
*Inhalation is main portal of entry |
||
* |
*Incubation 3 weeks to 3 months |
||
* |
*In outbreaks, 50% of exposed developed symptoms |
||
* |
*Primarily presents with pulmonary blastomycosis with influenza-like illness, acute pneumonia, ARDS, or chronic pneumonia |
||
* |
*Skin is most common extrapulmonary site, but can also infect bone and prostate |
||
* |
*CNS infection is rare |
||
=== |
===Coccidiomycosis=== |
||
* |
*Asymptaomtic common in 60% |
||
* |
*Early pulmonary infection |
||
** |
**Mild |
||
** |
**Valley fever, including arthralgias and erythema nodosum |
||
* |
*Extrapulmonary dissemination |
||
** |
**More common in African Americans |
||
=== |
===Emergomycosis=== |
||
* |
*Cutaneous disease in immunocompromised patients, especially advanced HIV |
||
* |
*Can also cause pulmonary disease, extrapulmonary disease, or disseminated |
||
== |
==Diagnosis== |
||
* |
*Notify laboratory if a [[Biosafety risk groups|risk group 3]] organism is suspected |
||
* |
*For blood cultures, the isolator system is preferred to BacTAlert |
||
* |
*Media |
||
** |
**Brain-heart infusion with sheep blood plus antibacterials is preferred |
||
** |
**Cycloheximide can be used to prevent growth of saprophytic molds (always with one plate without) |
||
** |
**Incubate at 30ºC to enhance growth of mold forms |
||
** |
**Incubated for 3 weeks for fungi in general, but should be extended to 4 weeks for dimorphic fungi |
||
*** |
***[[Coccidioides]] is the fastest-growing, within 3 to 5 days on SAB, and can grow on chocolate and sheep's blood agars |
||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
| Line 169: | Line 168: | ||
|} |
|} |
||
=== |
===EORTC Definition[[CiteRef::donnelly2019re]]=== |
||
* |
*'''Proven invasive fungal disease''' |
||
** |
**Histopathology or direct microscopy of sterile material of specimens obtained from an affected site showing the distinctive form of the fungus, or |
||
** |
**Recovery by culture of sterile material of the fungus from specimens from an affected site, or |
||
** |
**Blood culture that yields the fungus |
||
* |
*'''Probable invasive fungal disease''' |
||
** |
**Requires clinical features and mycologic evidence, but host does not have to be immunocompromised for dimorphic or endemic fungi |
||
** |
**Host factors: not applicable |
||
** |
**Clinical features: evidence for geographical or occupational exposure (including remote) to the fungus and compatible clinical illness |
||
** |
**Mycological evidence: |
||
*** |
***[[Histoplasma]] or [[Blastomyces]] antigen in urine, serum, or body fluid |
||
*** |
***Antibody to [[Coccidioides]] in CSF or 2-fold rise in 2 consecutive serum samples |
||
==Prevention== |
==Prevention== |
||
Latest revision as of 21:09, 7 March 2024
| Organism | Distribution | Diseases | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blastomyces | eastern US and Canada, with some reported in Africa | pulmonary infection, verrucous skin lesions, osteomyelitis, CNS infection | itraconazole (with amphotericin B induction if severe) |
| Coccidioides | southwestern US and parts of South and Central America | pulmonary infection, verrucous skin lesions, osteomyelitis, CNS infection | fluconazole (with amphotericin B and flucytosine induction if severe) |
| Histoplasma capsulatum | worldwide, including eastern North America, Central and South America, sub-Saharan Africa, and parts of Southeast Asia | pulmonary infection, CNS infection | itraconazole (with amphotericin B induction if severe) |
| Paracoccidioides brasiliensis | South America | pulmonary infection | itraconazole (with amphotericin B induction if severe) |
| Sporothrix schenckii | essentially worldwide | nodular lymphangitis | itraconazole |
| Talaromyces marneffei | Southeast Asia | disseminated (common in advanced HIV), pulmonary infection, abdominal abscess, skin lesions, osteomyelitis | amphotericin B induction followed by itraconazole |
Background
Microbiology
- Broad category of fungi that exist in a mold form at lower temperatures in the environment, and a yeast form at higher temperatures in the host body
- Cryptococcus does exhibit dimorphism, though it is predominately yeast and its dimorphism is not likely related to disease
- Often referred to as endemic fungi based on their geographic niches
- Includes the following genera and species:
- Blastomyces, including Blastomyces dermatitidis complex (Blastomyces dermatitidis and Blastomyces gilchristii), helices, silverae, parvus
- Histoplasma capsulatum (var. capsulatum and var. duboisii)
- Coccidiodes, including Coccidioides immitis and Coccidioides posadasii
- Paracoccidioides, including Paracoccidioides brasiliensis and Paracoccidioides lutzii
- Talaromyces marneffei
- Emergomyces, including Emergomyces pasteurianus, Emergomyces africanus, Emergomyces orientalis, Emergomyces canadensis, Emergomyces europaeus
- Sporothrix complex (Sporothrix brasiliensis, Sporothrix schenckii, Sporothrix globose, Sporothrix luriei)
Epidemiology
- Endemic dimorphic fungi are widely distributed1
Histoplasmosis
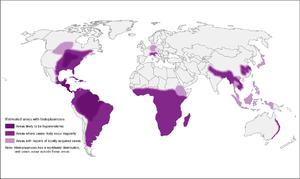
- High-endemic areas include Ohio and Mississippi river valley systems, but also in Central and South America
- However, 12-20% of cases in US occur outside of endemic areas
- In Canada, mostly along St. Lawrence seaway and Great Lakes drainage
- More recently, cases have been diagnosed in Alberta and Saskatchewan
- Also found in Asia and Africa, throughout, with var. duboisii in West Africa (mostly skin and soft tissue disease)
- Associated with soil contaminated by bird or bat guano
Coccidiomycosis
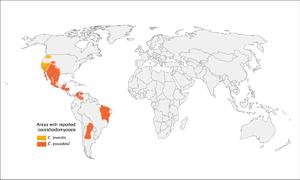
- More common in southwestern US, especially California and Arizona (but up to Washington state), as well as parts of South and Central America
- Concentrated heavily in San Joaquin Valley in California
- Present in soil
- High-risk activities: construction, military maneuvers, earthquakes/landslides, armadillo hunting, prisoners from other parts of the US that are incarcerated in California
Blastomycosis
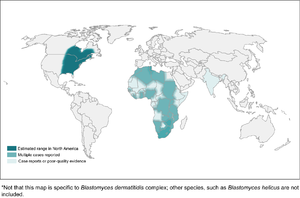
- Found mostly in eastern North America
- In Canada, found in northwestern Ontario, Quebec, Manitoba, and Saskatchewan
- Kenora is the hotspot in Canada
- In Canada, found in northwestern Ontario, Quebec, Manitoba, and Saskatchewan
- More common in wooded areas, damp soil, and near waterways
- High-risk activities include excavation and construction
Emergomycosis
- Different species found worldwide, including Emergomyces canadensis in Saskatchewan, Colorado, and New Mexico
- More common in HIV patients or other immunocompromised
Clinical Manifestations
Histoplasmosis
| Acute Pulmonary | Cavitary and Chronic Pulmonary | Progressive Disseminated | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical | usually asymptomatic or mild; can have non-pleuritic chest pain from mediastinal or hilar lymphadenopathy; can have rheumatic features or pericarditis | 8% develop fibrocavitary disease, associated with underlying COPD | |
| Immunology | >90% positive skin test, 20% urine antigen | 75-95% antibodyes, 40% urine antigen | 60-90% urine antigen |
| Culture | <25% positive | 5-70% positive (more likely if cavitary) | 50-70% positive |
Blastomycosis
- Inhalation is main portal of entry
- Incubation 3 weeks to 3 months
- In outbreaks, 50% of exposed developed symptoms
- Primarily presents with pulmonary blastomycosis with influenza-like illness, acute pneumonia, ARDS, or chronic pneumonia
- Skin is most common extrapulmonary site, but can also infect bone and prostate
- CNS infection is rare
Coccidiomycosis
- Asymptaomtic common in 60%
- Early pulmonary infection
- Mild
- Valley fever, including arthralgias and erythema nodosum
- Extrapulmonary dissemination
- More common in African Americans
Emergomycosis
- Cutaneous disease in immunocompromised patients, especially advanced HIV
- Can also cause pulmonary disease, extrapulmonary disease, or disseminated
Diagnosis
- Notify laboratory if a risk group 3 organism is suspected
- For blood cultures, the isolator system is preferred to BacTAlert
- Media
- Brain-heart infusion with sheep blood plus antibacterials is preferred
- Cycloheximide can be used to prevent growth of saprophytic molds (always with one plate without)
- Incubate at 30ºC to enhance growth of mold forms
- Incubated for 3 weeks for fungi in general, but should be extended to 4 weeks for dimorphic fungi
- Coccidioides is the fastest-growing, within 3 to 5 days on SAB, and can grow on chocolate and sheep's blood agars
| Organism | Findings on Microscopy |
|---|---|
| Histoplasma | intracellular 2-4 μm yeast-like cells in macrophages, may have narrow-based budding |
| Blastomyces | 8-15 μm yeast-like cells with broad-based budding, refractile thick cell wall, but early spherules can be confused with Coccioides |
| Coccidioides | spherules are thick-walled, 10-80 μm with endospores; alternating barrel-shaped arthroconidia in mycelial form |
| Marneffei | divides by binary fission |
| Emergomyces | 2.5-5 μm small yeast form with narrow-based budding; septate hyphae with conidiophores at right answers, with conidia clustered in florettes of 2 to 3 conidia |
EORTC Definition2
- Proven invasive fungal disease
- Histopathology or direct microscopy of sterile material of specimens obtained from an affected site showing the distinctive form of the fungus, or
- Recovery by culture of sterile material of the fungus from specimens from an affected site, or
- Blood culture that yields the fungus
- Probable invasive fungal disease
- Requires clinical features and mycologic evidence, but host does not have to be immunocompromised for dimorphic or endemic fungi
- Host factors: not applicable
- Clinical features: evidence for geographical or occupational exposure (including remote) to the fungus and compatible clinical illness
- Mycological evidence:
- Histoplasma or Blastomyces antigen in urine, serum, or body fluid
- Antibody to Coccidioides in CSF or 2-fold rise in 2 consecutive serum samples
Prevention
Laboratory Safety
- Many are risk group 3 and need to notify lab if suspected
- Opening the plates outside of a BSC is one of the highest risk actions
References
- ^ Ashraf N, Kubat RC, Poplin V, Adenis AA, Denning DW, Wright L, McCotter O, Schwartz IS, Jackson BR, Chiller T, Bahr NC. Re-drawing the Maps for Endemic Mycoses.. Mycopathologia. 2020. doi:10.1007/s11046-020-00431-2. PMID 32040709.