Dimorphic fungi: Difference between revisions
From IDWiki
Content deleted Content added
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Background== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
===Microbiology=== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*[[Cryptococcus]] does exhibit dimorphism, though it is predominately yeast and its dimorphism is not likely related to disease |
*[[Cryptococcus]] does exhibit dimorphism, though it is predominately yeast and its dimorphism is not likely related to disease |
||
*Often referred to as endemic fungi based on their geographic niches |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
| Line 38: | Line 41: | ||
|[[amphotericin B]] induction followed by [[itraconazole]] |
|[[amphotericin B]] induction followed by [[itraconazole]] |
||
|} |
|} |
||
==Distribution== |
|||
* [[Blastomyces species]], including Blastomyces dermatitidis complex ([[Blastomyces dermatitidis]] and [[Blastomyces gilchristii]]), helices, silverae, parvus |
|||
* [[Histoplasmosis capsulatum]] (var. ''capsulatum'' and var. ''duboisii'') |
|||
* [[Coccidiodes species]], including [[Coccidioides immitis]] and [[Coccidioides posadasii]] |
|||
* [[Paracoccidioides species]], including [[Paracoccidioides brasiliensis]] and [[Paracoccidioides lutzii]] |
|||
* [[Talaromyces marneffei]] |
|||
* [[Emergomyces species]], including [[Emergomyces pasteurianus]], [[Emergomyces africanus]], [[Emergomyces orientalis]], [[Emergomyces canadensis]], [[Emergomyces europaeus]] |
|||
* [[Sporothrix species]] complex (Sporothrix brasiliensis, Sporothrix schenckii, Sporothrix globose, Sporothrix luriei) |
|||
===Epidemiology=== |
|||
*Endemic dimorphic fungi are widely distributed[[CiteRef::PMID32040709]] |
*Endemic dimorphic fungi are widely distributed[[CiteRef::PMID32040709]] |
||
=== |
====Histoplasmosis==== |
||
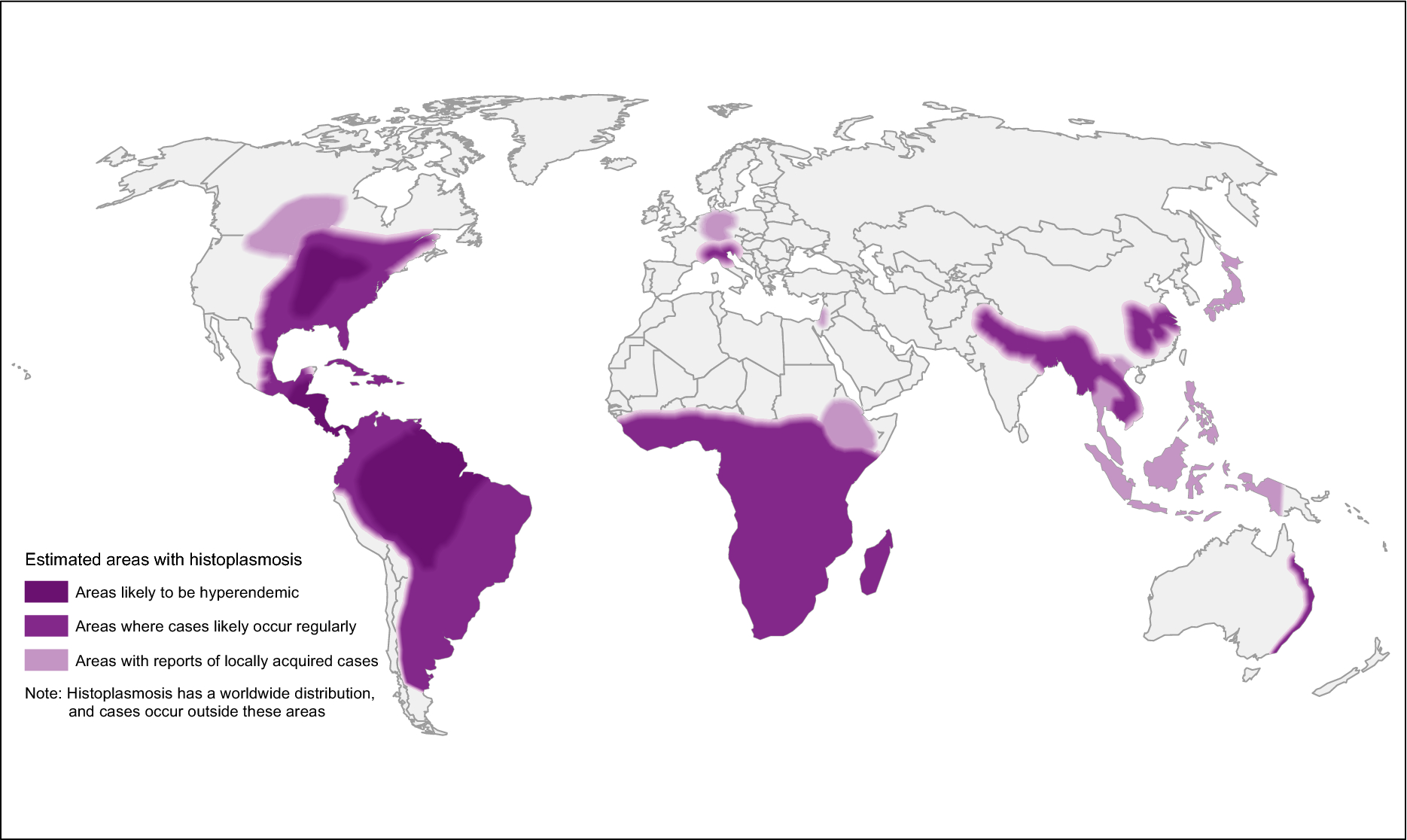
[[File:Histoplasmosis_map.png|frame|Histoplasmosis]] |
[[File:Histoplasmosis_map.png|frame|Histoplasmosis]] |
||
=== |
====Coccidiomycosis==== |
||
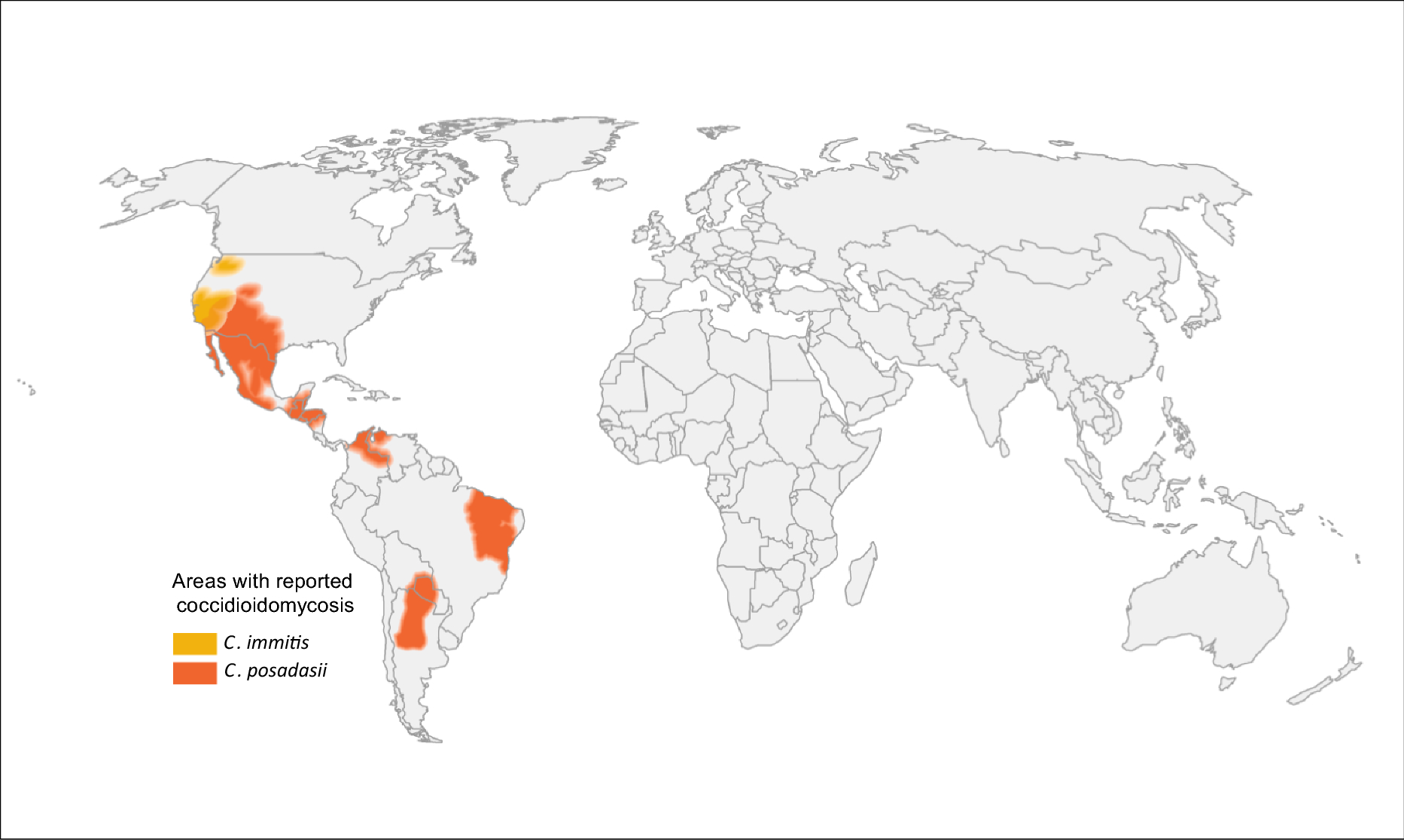
[[File:Coccidiomycosis_map.png|frame|Coccidiomycosis]] |
[[File:Coccidiomycosis_map.png|frame|Coccidiomycosis]] |
||
=== |
====Blastomycosis==== |
||
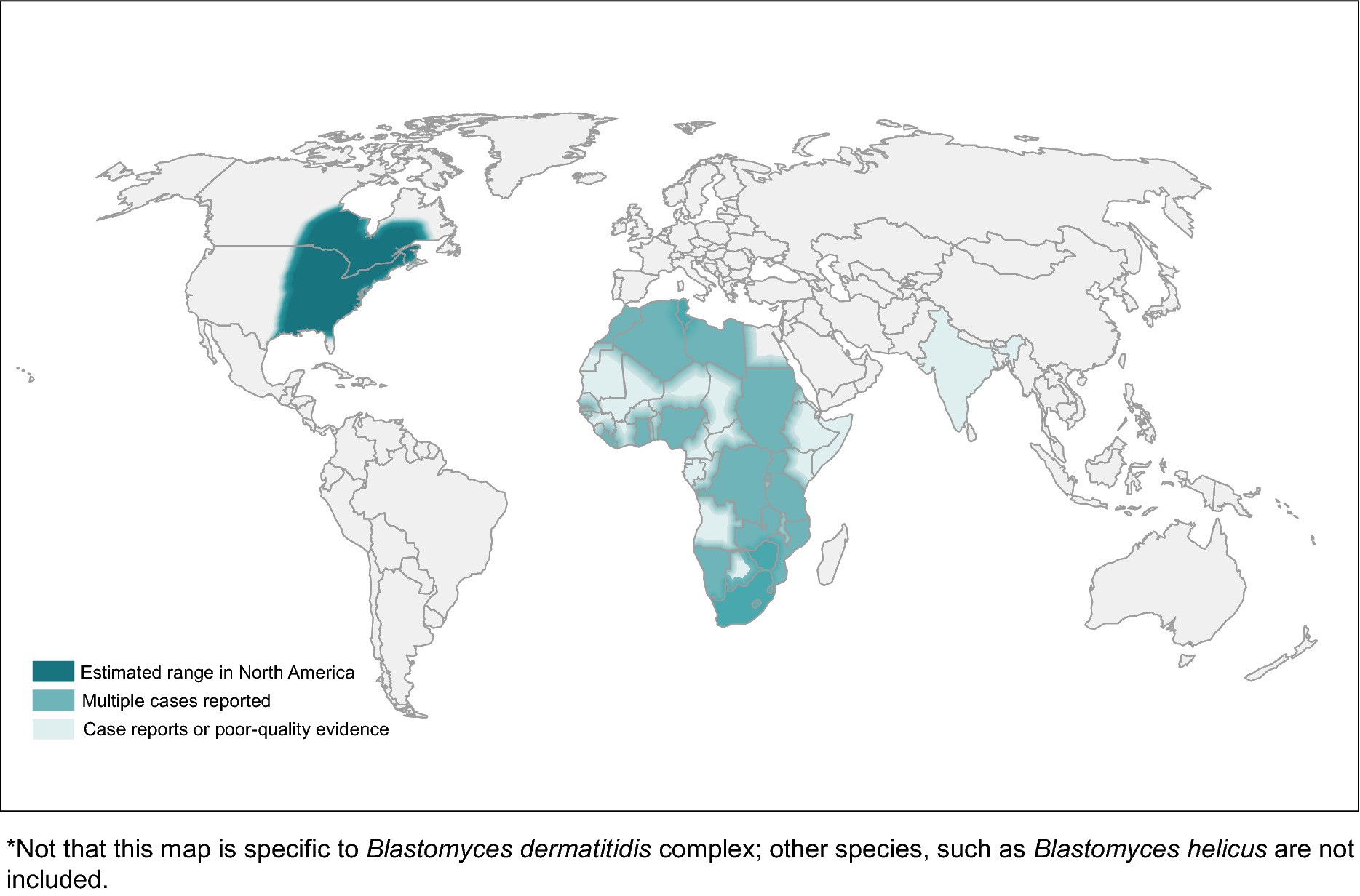
[[File:Blastomycosis_map.png|frame|Blastomycosis]] |
[[File:Blastomycosis_map.png|frame|Blastomycosis]] |
||
== Prevention == |
|||
=== Laboratory Safety === |
|||
* Many are risk group 3 and need to notify lab if suspected |
|||
* Opening the plates outside of a BSC is one of the highest risk actions |
|||
[[Category:Fungi]] |
|||
Revision as of 14:38, 29 October 2020
Background
Microbiology
- Broad category of fungi that exist in a mold form at lower temperatures in the environment, and a yeast form at higher temperatures in the host body
- Cryptococcus does exhibit dimorphism, though it is predominately yeast and its dimorphism is not likely related to disease
- Often referred to as endemic fungi based on their geographic niches
| Organism | Distribution | Diseases | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blastomyces species | eastern US and Canada, with some reported in Africa | pulmonary infection, verrucous skin lesions, osteomyelitis, CNS infection | itraconazole (with amphotericin B induction if severe) |
| Coccidioides species | southwestern US and parts of South and Central America | pulmonary infection, verrucous skin lesions, osteomyelitis, CNS infection | fluconazole (with amphotericin B and flucytosine induction if severe) |
| Histoplasma capsulatum | worldwide, including eastern North America, Central and South America, sub-Saharan Africa, and parts of Southeast Asia | pulmonary infection, CNS infection | itraconazole (with amphotericin B induction if severe) |
| Paracoccidioides brasiliensis | South America | pulmonary infection | itraconazole (with amphotericin B induction if severe) |
| Sporothrix schenckii | essentially worldwide | nodular lymphangitis | itraconazole |
| Talaromyces marneffei | Southeast Asia | disseminated (common in advanced HIV), pulmonary infection, abdominal abscess, skin lesions, osteomyelitis | amphotericin B induction followed by itraconazole |
- Blastomyces species, including Blastomyces dermatitidis complex (Blastomyces dermatitidis and Blastomyces gilchristii), helices, silverae, parvus
- Histoplasmosis capsulatum (var. capsulatum and var. duboisii)
- Coccidiodes species, including Coccidioides immitis and Coccidioides posadasii
- Paracoccidioides species, including Paracoccidioides brasiliensis and Paracoccidioides lutzii
- Talaromyces marneffei
- Emergomyces species, including Emergomyces pasteurianus, Emergomyces africanus, Emergomyces orientalis, Emergomyces canadensis, Emergomyces europaeus
- Sporothrix species complex (Sporothrix brasiliensis, Sporothrix schenckii, Sporothrix globose, Sporothrix luriei)
Epidemiology
- Endemic dimorphic fungi are widely distributed1
Histoplasmosis
Coccidiomycosis
Blastomycosis
Prevention
Laboratory Safety
- Many are risk group 3 and need to notify lab if suspected
- Opening the plates outside of a BSC is one of the highest risk actions
References
- ^ Ashraf N, Kubat RC, Poplin V, Adenis AA, Denning DW, Wright L, McCotter O, Schwartz IS, Jackson BR, Chiller T, Bahr NC. Re-drawing the Maps for Endemic Mycoses.. Mycopathologia. 2020. doi:10.1007/s11046-020-00431-2. PMID 32040709.