Histoplasma capsulatum: Difference between revisions
From IDWiki
Histoplasma capsulatum
Content deleted Content added
No edit summary |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
===Microbiology=== |
===Microbiology=== |
||
*Saprophytic environmental fungus withing the family Ascomycetes |
|||
*Dimorphic fungus; mold at room temperature, yeast at >37º C |
|||
*Thermally dimorphic, existing as a mold <35ºC and a yeast at >37ºC |
|||
**Mold: aerial hyphae with macroconidia |
|||
**Mold |
|||
***Mold form is highly infectious, associated with lab-related outbreaks |
***Mold form is highly infectious, associated with lab-related outbreaks |
||
***Septate hyaline mold with aerial hyphae with macroconidia, which are its identifying feature |
|||
***Mycelia have a typical appearance of spiked spherical conidia |
|||
***Two types of conidia: tuberculate macroconidia (ovoid bodies 8 to 15 μm with spikes), and microconidia (small, smooth oval bodies 2 to 5 μm) |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
***Two colony types, brown (B) and albino (A) |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
***Non-infectious, once hanging out in your body |
***Non-infectious, once hanging out in your body |
||
***Small, 2 to 5 μm |
|||
***Narrow-based budding |
|||
***Demonstrates multipolar narrow-based budding |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
***Does not look particularly different from other yeast, but may be intracellular |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*Three variants |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
**''H. capsulatum'' var. ''farciminosum'' |
|||
===Epidemiology=== |
===Epidemiology=== |
||
| Line 17: | Line 24: | ||
*Endemic in many parts of the world |
*Endemic in many parts of the world |
||
**Ohio and Mississippi River Valley systems (Central/Eastern US) |
**Ohio and Mississippi River Valley systems (Central/Eastern US), where seroprevalence is as high as 80% in adults |
||
**Probably up through St. Lawrence River as well |
**Probably up through St. Lawrence River as well |
||
**Probably more broadly distributed, including Central and South America, South and East Asia, and Australia |
**Probably more broadly distributed, including Central and South America, South and East Asia, and Australia |
||
| Line 24: | Line 31: | ||
**Disturbing the soil aerosolizes it, allowing the microconidia to be inhaled |
**Disturbing the soil aerosolizes it, allowing the microconidia to be inhaled |
||
**Microconidia can be transported for miles by air currents |
**Microconidia can be transported for miles by air currents |
||
===Risk Factors=== |
|||
*HIV, solid organ transplant, hematologic transplant |
|||
*Primary immunodeficiencies: X-linked hypogammaglobulinemia |
|||
===Pathophysiology=== |
===Pathophysiology=== |
||
| Line 30: | Line 42: | ||
**Innoculum size can be smaller with immunodeficiency |
**Innoculum size can be smaller with immunodeficiency |
||
**Size of innoculation affects disease severity and progression |
**Size of innoculation affects disease severity and progression |
||
*Microconidia transform into budding yeasts, in a process that is dependent on macrophage calcium and iron |
*Microconidia transform into budding yeasts, in a process that is dependent on intracellular macrophage calcium and iron |
||
*They multiply inside macrophages, and translocate through the lymphatics |
*They multiply inside macrophages, and translocate through the lymphatics |
||
*Cellular immunity developed around 2 weeks later |
*Cellular immunity developed around 2 weeks later |
||
**Response depends on IL-12 and TNF- |
**Response depends on IL-12 and TNF-α |
||
**Organize to form granulomas to contain the infection |
**Organize to form granulomas to contain the infection |
||
*Latent infection can reactivate, but rare |
*Latent infection can reactivate, but rare |
||
**Most common with infliximab |
**Most common with [[infliximab]] |
||
*In impaired cellular immunity, infection can become disseminated |
*In impaired cellular immunity, infection can become disseminated |
||
==Clinical Manifestations== |
==Clinical Manifestations== |
||
*Spectrum of illness, related to the size of the inoculum, strain-specific virulence, and host immunity |
|||
*Often asymptomatic; in endemic areas, 50-80% of people skin-test positive or have radiographic evidence of previous infection |
*Often asymptomatic; in endemic areas, 50-80% of people skin-test positive or have radiographic evidence of previous infection |
||
*Can cross tissue planes |
*Can cross tissue planes |
||
===Acute |
===Acute Pulmonary Histoplasmosis=== |
||
*Fever, chill, malaise, headaches, myalgias, anorexia, cough, dyspnea, and chest pain |
*Fever, chill, malaise, headaches, myalgias, anorexia, cough, dyspnea, and chest pain |
||
**Spectrum from mild to severe |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*Pneumonitis on chest x-ray, often with adenopathy |
*Pneumonitis on chest x-ray, often with adenopathy |
||
**"Buckshot" appearance? (Mandell) |
**"Buckshot" appearance? (Mandell) |
||
| Line 52: | Line 67: | ||
*Can have pericarditis from the inflammatory response |
*Can have pericarditis from the inflammatory response |
||
*Hilar adenopathy can necrotize |
*Hilar adenopathy can necrotize |
||
| ⚫ | |||
===Progressive |
===Progressive Disseminated Histoplasmosis=== |
||
*Usually, though not exclusively, in immunocompromised |
*Usually, though not exclusively, in immunocompromised patients |
||
**Risk factors include CD4 <200, very old or very young, and therapeutic immunosuppression ( |
**Risk factors include CD4 <200, very old or very young, and therapeutic immunosuppression ([[prednisone]], [[MMF]], [[tacrolimus]], [[methotrexate]], [[TNF-α inhibitors]], other biologics) |
||
*Can be rapidly-progressing and acute, or more subacute |
*Can be rapidly-progressing and acute, or more subacute |
||
===Acute |
===Acute Progressive Disseminated Histoplasmosis=== |
||
*Fever, weight loss, organomegaly, thrombocytopenia |
*Fever, weight loss, organomegaly, thrombocytopenia |
||
| Line 67: | Line 81: | ||
*Adrenal insufficiency |
*Adrenal insufficiency |
||
===Chronic |
===Chronic Progressive Disseminated Histoplasmosis=== |
||
*In normal hosts |
*In normal hosts |
||
| Line 76: | Line 90: | ||
*Can also have hepatosplenomegaly, chronic meningitis, or chronic granulomatous hepatitis |
*Can also have hepatosplenomegaly, chronic meningitis, or chronic granulomatous hepatitis |
||
===Chronic |
===Chronic Cavitary Histoplasmosis=== |
||
*Typically seen in bullous emphysema |
*Typically seen in bullous emphysema |
||
| Line 84: | Line 98: | ||
*Chest x-ray shows upper-lobe infiltrations, vacitation, and pleural thickening, similar to tuberculosis |
*Chest x-ray shows upper-lobe infiltrations, vacitation, and pleural thickening, similar to tuberculosis |
||
===Fibrosing |
===Fibrosing Mediastinitis=== |
||
*Histoplasmosis is the most common cause of [[fibrosing mediastinitis]] |
|||
*Rare but serious |
*Rare but serious |
||
*Progressive fibrosis around hilar/ |
*Progressive fibrosis around hilar/mediastinal lymphadenopathy, wither unilateral or bilateral |
||
**Occludes central vessels and airways |
|||
*Can present with a SVC syndrome, obstruction of pulmonary vessels, or airway obstruction |
*Can present with a SVC syndrome, obstruction of pulmonary vessels, or airway obstruction |
||
*Can also present with recurrent pneumonias, hemoptysis, or respiratory failure |
*Can also present with recurrent pneumonias, hemoptysis, or respiratory failure |
||
*30% mortality |
*30% mortality |
||
===Other |
===Other Complications=== |
||
*Ophthalmic uveitis |
*Ophthalmic posterior [[uveitis]] |
||
*Meningitis |
*Meningitis |
||
*[[Infective endocarditis]] |
|||
*Endocarditis |
|||
==African |
===African Histoplasmosis=== |
||
*''H. capsulatum'' vars. ''capsulatum'' and ''duboisii'' coexist in Africa |
*''H. capsulatum'' vars. ''capsulatum'' and ''duboisii'' coexist in Africa |
||
| Line 114: | Line 130: | ||
==Diagnosis== |
==Diagnosis== |
||
*Histopathology of biopsy specimens |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
**Caseating and non-caseating granulomas |
|||
**Mold and yeast forms depending on the temperature |
**Mold and yeast forms depending on the temperature |
||
**Best stain is GMS ( |
***Best stain is GMS (Gomori methenamine silver) |
||
**Seen within the macrophages |
***Seen within the macrophages |
||
| ⚫ | |||
**Usually grows within 7 days, and almost always within 21 days |
|||
**Need to use lysis centrifugation system to release intracellular pathogens before culture |
|||
**Yield of 15% for acute pulmonary, but cavitary is 60% and up to 90% in advanced HIV with bronchoscopy |
|||
**Bone marrow and blood cultures are 50% sensitive |
|||
**Sensitivity increases with volume and number of samples |
|||
*Serology can be done for antigen or antibody |
*Serology can be done for antigen or antibody |
||
**Serology for antibodies by complement fixation |
|||
**Serology for antibodies by agar gel precipitin test |
|||
***Anti-H is uncommon (<10% of patients), but signifies active infection |
|||
***Anti-M is common (up to 80% of patients), but signifies either active or recovered infection |
|||
**Serology may be negative in immunosuppressed patients |
**Serology may be negative in immunosuppressed patients |
||
**Antigen of '''urine''' (best), BAL fluid, and serum if available |
**Antigen of '''urine''' (best), BAL fluid, and serum if available |
||
***Urine is best, but only 40% sensitive in cavitary, up to 95% in AIDS patients |
***Urine is best, but only 40% sensitive in cavitary, up to 95% in AIDS patients |
||
****However, this may no longer be the case, with overall sensitivity of 80% and specificity of 90% regardless of sample source |
|||
***Cross-reacts with other endemic fungi; false-positives with antithymocyte globulin |
***Cross-reacts with other endemic fungi; false-positives with antithymocyte globulin |
||
*PCR is possible |
*PCR is possible |
||
| Line 129: | Line 157: | ||
*In general, mild infections are treated with [[Is treated by::itraconazole]] and severe infections with [[Is treated by::amphotericin B]] |
*In general, mild infections are treated with [[Is treated by::itraconazole]] and severe infections with [[Is treated by::amphotericin B]] |
||
**Give tablets of [[itraconazole]] with acidic drink, such as can of soda, and avoid antacids |
|||
**[[Itraconazole]] requires therapeutic drug monitoring |
|||
*[[Is treated by::Voriconazole]] is an easier-to-prescribe alternative that is likely as effective as [[itraconazole]] |
|||
*Indications for antifungal therapy |
|||
**'''Definitely:''' moderate to severe acute diffuse pulmonary infection, chronic cavitary pulmonary disease, disseminated disease, CNS infection |
|||
**'''Possibly/uncertain:''' asymptomatic, mild symptoms lasting longer than 1 month, acute focal pulmonary infection, mediastinal lymphadenitis, mediastinal granuloma |
|||
**'''Not recommended:''' mediastinal fibrosis, pulmonary nodule, broncholithiasis, presumed ocular histoplasmosis syndrome |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
| Line 134: | Line 169: | ||
!Treatment |
!Treatment |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|Acute pulmonary histoplasmosis |
| colspan="2" |'''Acute pulmonary histoplasmosis''' |
||
| |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| Mild, self-resolving |
| Mild, self-resolving |
||
| Line 144: | Line 178: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
| Moderate to severe |
| Moderate to severe |
||
|[[Liposomal amphotericin B]] 3-5 mg/kg/d for 1-2 weeks, followed by [[itraconazole]] 200 mg TID x3d then [[itraconazole]] 200 mg BID x12wk<br /> |
|[[Liposomal amphotericin B]] 3-5 mg/kg/d for 1-2 weeks, followed by [[itraconazole]] 200 mg TID x3d then [[itraconazole]] 200 mg BID x12wk<br />[[Methylprednisolone]] 0.5-1 mg/kg IV daily for first 1-2 weeks if respiratory complications |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|Chronic cavitary pulmonary histoplasmosis |
|Chronic cavitary pulmonary histoplasmosis |
||
|[[Itraconazole]] 200 mg TID x3d then daily or BID for at least 1 year (18-24 months may have lower relapse) |
|[[Itraconazole]] 200 mg TID x3d then daily or BID for at least 1 year (18-24 months may have lower relapse) |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|Complications |
| colspan="2" |'''Complications''' |
||
| |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| Pericarditis |
| Pericarditis |
||
|NSAIDs if mild<br />Prednisone 0.5-1 mg/kg daily then taper over 1-2 weeks, plus |
|NSAIDs if mild<br />[[Prednisone]] 0.5-1 mg/kg daily then taper over 1-2 weeks, plus [[itraconazole]] (as above) for 6-12 weeks if hemodynamic compromise<br />May need therapeutic pericardiocentesis |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Rheumatologic |
| Rheumatologic |
||
|NSAIDs if mild, prednisone and [[itraconazole]] (as for pericarditis) if severe |
|NSAIDs if mild, [[prednisone]] and [[itraconazole]] (as for pericarditis) if severe |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Mediastinal lymphadenitis |
| Mediastinal lymphadenitis |
||
| Line 164: | Line 197: | ||
|Usually no treatment. Standard [[itraconazole]] protocol for 6-12 weeks if symptomatic. |
|Usually no treatment. Standard [[itraconazole]] protocol for 6-12 weeks if symptomatic. |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Fibrosing mediastinitis|Mediastinal fibrosis]] |
|||
| Mediastinal fibrosis |
|||
|Antifungals not recommended. Treat only if there is suspicion of mediastinal granuloma. May need stenting of obstructed pulmonary vessels. |
|Antifungals not recommended. Treat only if there is suspicion of mediastinal granuloma. May need stenting of obstructed pulmonary vessels. |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 170: | Line 203: | ||
|Antifungals not recommended. May need surgery. |
|Antifungals not recommended. May need surgery. |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis |
|'''Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis''' |
||
|Follow antigen levels during therapy and for 12 months after to monitor for relapse |
|Follow antigen levels during therapy and for 12 months after to monitor for relapse |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 192: | Line 225: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
|Prophylaxis |
|Prophylaxis |
||
|[[Itraconazole]] 200 mg po daily recommended if HIV with CD4 <150 and more than 10 cases per 100 patient-years |
|[[Itraconazole]] 200 mg po daily recommended if [[HIV]] with CD4 <150 and more than 10 cases per 100 patient-years |
||
|} |
|} |
||
'''Note:''' therapeutic drug level monitoring is recommended for itraconazole |
*'''Note:''' therapeutic drug level monitoring is recommended for itraconazole |
||
| ⚫ | |||
==Prevention== |
|||
===Lab Safety=== |
|||
*[[Biosafety risk groups|Biosafety risk group 3]] organism, so needs BSL 3 |
|||
*Should be suspected with any white mold |
|||
===Prophylaxis=== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*May be indicated for endemic areas in patients with advanced HIV and low CD4 count |
|||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:''Histoplasma capsulatum''}} |
{{DISPLAYTITLE:''Histoplasma capsulatum''}} |
||
[[Category:Dimorphic fungi]] |
[[Category:Dimorphic fungi]] |
||
Latest revision as of 15:05, 29 October 2020
Background
Microbiology
- Saprophytic environmental fungus withing the family Ascomycetes
- Thermally dimorphic, existing as a mold <35ºC and a yeast at >37ºC
- Mold
- Mold form is highly infectious, associated with lab-related outbreaks
- Septate hyaline mold with aerial hyphae with macroconidia, which are its identifying feature
- Two types of conidia: tuberculate macroconidia (ovoid bodies 8 to 15 μm with spikes), and microconidia (small, smooth oval bodies 2 to 5 μm)
- Two colony types, brown (B) and albino (A)
- Yeast
- Non-infectious, once hanging out in your body
- Small, 2 to 5 μm
- Demonstrates multipolar narrow-based budding
- Does not look particularly different from other yeast, but may be intracellular
- Mold
- Three variants
- H. capsulatum var. capsulatum, which is the most common worldwide, and is further divided into various clades
- H. capsulatum var. duboisii which is only present in western Africa, and has larger yeast forms
- Can take up to 7 days to grow
- H. capsulatum var. farciminosum
Epidemiology
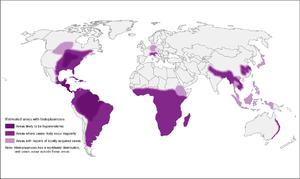
- Endemic in many parts of the world
- Ohio and Mississippi River Valley systems (Central/Eastern US), where seroprevalence is as high as 80% in adults
- Probably up through St. Lawrence River as well
- Probably more broadly distributed, including Central and South America, South and East Asia, and Australia
- H. capsulatum var. duboisii in western Africa
- Typically found in moist soil enriched with bat or bird droppings, which helps it to sporulate
- Disturbing the soil aerosolizes it, allowing the microconidia to be inhaled
- Microconidia can be transported for miles by air currents
Risk Factors
- HIV, solid organ transplant, hematologic transplant
- Primary immunodeficiencies: X-linked hypogammaglobulinemia
Pathophysiology
- Inhaled microconidia reach the alveolii and are phagocytosed by alveolar macrophages
- Innoculum size can be smaller with immunodeficiency
- Size of innoculation affects disease severity and progression
- Microconidia transform into budding yeasts, in a process that is dependent on intracellular macrophage calcium and iron
- They multiply inside macrophages, and translocate through the lymphatics
- Cellular immunity developed around 2 weeks later
- Response depends on IL-12 and TNF-α
- Organize to form granulomas to contain the infection
- Latent infection can reactivate, but rare
- Most common with infliximab
- In impaired cellular immunity, infection can become disseminated
Clinical Manifestations
- Spectrum of illness, related to the size of the inoculum, strain-specific virulence, and host immunity
- Often asymptomatic; in endemic areas, 50-80% of people skin-test positive or have radiographic evidence of previous infection
- Can cross tissue planes
Acute Pulmonary Histoplasmosis
- Fever, chill, malaise, headaches, myalgias, anorexia, cough, dyspnea, and chest pain
- Spectrum from mild to severe
- Usually self-limited, no need to treat unless longer than a month
- Pneumonitis on chest x-ray, often with adenopathy
- "Buckshot" appearance? (Mandell)
- Can have rheumatologic sequelae in 5-10%, with arthralgias, arthritis, and erythema nodosum
- Can have pericarditis from the inflammatory response
- Hilar adenopathy can necrotize
Progressive Disseminated Histoplasmosis
- Usually, though not exclusively, in immunocompromised patients
- Risk factors include CD4 <200, very old or very young, and therapeutic immunosuppression (prednisone, MMF, tacrolimus, methotrexate, TNF-α inhibitors, other biologics)
- Can be rapidly-progressing and acute, or more subacute
Acute Progressive Disseminated Histoplasmosis
- Fever, weight loss, organomegaly, thrombocytopenia
- Meningitis or focal brain lesions
- Oral and GI mucosal ulcerations
- Adrenal insufficiency
Chronic Progressive Disseminated Histoplasmosis
- In normal hosts
- Absent or low-grade fever
- Longer course
- Most common finding is oropharyngeal lesion: deep, well-circumscribed, unrated, and painless
- Mimics squamous cell carcinoma
- Can also have hepatosplenomegaly, chronic meningitis, or chronic granulomatous hepatitis
Chronic Cavitary Histoplasmosis
- Typically seen in bullous emphysema
- Productive cough, dyspnea, low-grade fever, night sweats, weight loss
- Hemoptysis is rare
- Progressive without treatment
- Chest x-ray shows upper-lobe infiltrations, vacitation, and pleural thickening, similar to tuberculosis
Fibrosing Mediastinitis
- Histoplasmosis is the most common cause of fibrosing mediastinitis
- Rare but serious
- Progressive fibrosis around hilar/mediastinal lymphadenopathy, wither unilateral or bilateral
- Occludes central vessels and airways
- Can present with a SVC syndrome, obstruction of pulmonary vessels, or airway obstruction
- Can also present with recurrent pneumonias, hemoptysis, or respiratory failure
- 30% mortality
Other Complications
- Ophthalmic posterior uveitis
- Meningitis
- Infective endocarditis
African Histoplasmosis
- H. capsulatum vars. capsulatum and duboisii coexist in Africa
- var. duboisii has more skin and skeletal manifestations
- Ulcers, nodules, or psoriaform lesions that can spontaneously resolve
- Can cause a cold abscess, without inflammation
- Osteolytic bone lesions are common (50%) of cases
- Skull and ribs most common
- Can have sinus formation and cystic bone lesions
- May not have any evidence on CXR of prior pulmonary histoplasmosis
- Can also present with progressive disseminated disease, with fevers and multiorgan involvement
- Combianation of granulomas and pus
- Larger yeast is harder for macrophages to engulf
- Ulcers, nodules, or psoriaform lesions that can spontaneously resolve
Diagnosis
- Histopathology of biopsy specimens
- Caseating and non-caseating granulomas
- Mold and yeast forms depending on the temperature
- Best stain is GMS (Gomori methenamine silver)
- Seen within the macrophages
- Fungal culture of sputum (chronic cavitary), or blood or bone marrow aspirate (disseminated), or CSF (CNS histo)
- Usually grows within 7 days, and almost always within 21 days
- Need to use lysis centrifugation system to release intracellular pathogens before culture
- Yield of 15% for acute pulmonary, but cavitary is 60% and up to 90% in advanced HIV with bronchoscopy
- Bone marrow and blood cultures are 50% sensitive
- Sensitivity increases with volume and number of samples
- Serology can be done for antigen or antibody
- Serology for antibodies by complement fixation
- Serology for antibodies by agar gel precipitin test
- Anti-H is uncommon (<10% of patients), but signifies active infection
- Anti-M is common (up to 80% of patients), but signifies either active or recovered infection
- Serology may be negative in immunosuppressed patients
- Antigen of urine (best), BAL fluid, and serum if available
- Urine is best, but only 40% sensitive in cavitary, up to 95% in AIDS patients
- However, this may no longer be the case, with overall sensitivity of 80% and specificity of 90% regardless of sample source
- Cross-reacts with other endemic fungi; false-positives with antithymocyte globulin
- Urine is best, but only 40% sensitive in cavitary, up to 95% in AIDS patients
- PCR is possible
- 16S PCR
Management
- In general, mild infections are treated with itraconazole and severe infections with amphotericin B
- Give tablets of itraconazole with acidic drink, such as can of soda, and avoid antacids
- Itraconazole requires therapeutic drug monitoring
- Voriconazole is an easier-to-prescribe alternative that is likely as effective as itraconazole
- Indications for antifungal therapy
- Definitely: moderate to severe acute diffuse pulmonary infection, chronic cavitary pulmonary disease, disseminated disease, CNS infection
- Possibly/uncertain: asymptomatic, mild symptoms lasting longer than 1 month, acute focal pulmonary infection, mediastinal lymphadenitis, mediastinal granuloma
- Not recommended: mediastinal fibrosis, pulmonary nodule, broncholithiasis, presumed ocular histoplasmosis syndrome
| Syndrome | Treatment |
|---|---|
| Acute pulmonary histoplasmosis | |
| Mild, self-resolving | If resolves within a month, no need to treat |
| Mild, ongoing symptoms | Itraconazole 200 mg po TID x3d then itra 200 mg po daily or BID for 6-12 weeks |
| Moderate to severe | Liposomal amphotericin B 3-5 mg/kg/d for 1-2 weeks, followed by itraconazole 200 mg TID x3d then itraconazole 200 mg BID x12wk Methylprednisolone 0.5-1 mg/kg IV daily for first 1-2 weeks if respiratory complications |
| Chronic cavitary pulmonary histoplasmosis | Itraconazole 200 mg TID x3d then daily or BID for at least 1 year (18-24 months may have lower relapse) |
| Complications | |
| Pericarditis | NSAIDs if mild Prednisone 0.5-1 mg/kg daily then taper over 1-2 weeks, plus itraconazole (as above) for 6-12 weeks if hemodynamic compromise May need therapeutic pericardiocentesis |
| Rheumatologic | NSAIDs if mild, prednisone and itraconazole (as for pericarditis) if severe |
| Mediastinal lymphadenitis | Usually no treatment. Follow guide for acute pulmonary histoplasmosis. |
| Mediastinal granuloma | Usually no treatment. Standard itraconazole protocol for 6-12 weeks if symptomatic. |
| Mediastinal fibrosis | Antifungals not recommended. Treat only if there is suspicion of mediastinal granuloma. May need stenting of obstructed pulmonary vessels. |
| Broncholithiasis | Antifungals not recommended. May need surgery. |
| Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis | Follow antigen levels during therapy and for 12 months after to monitor for relapse |
| Mild to moderate | Itraconazole for 12 months |
| Moderately severe to severe | Liposomal amphotericin B 3 mg/kg for 1-2 weeks then oral itraconazole for at least 12 months |
| Immunosuppressed | May need lifelong suppressive therapy with itraconazole 200 mg po daily |
| CNS histoplasmosis | Liposomal amphotericin B 5 mg/kg daily for 4-6 weeks (total 175 mg/kg) followed by itraconazole for at least 1 year, until resolution of CSF abnormalities |
| Pregnancy | Liposomal amphotericin B 3-5 mg/kg for 4-6 weeks |
| Children | As per above guidelines, with amphotericin B deoxycholate 1 mg/kg and itraconazole 2.5-5 mg/kg bid (max 400 mg daily) |
| Prophylaxis | Itraconazole 200 mg po daily recommended if HIV with CD4 <150 and more than 10 cases per 100 patient-years |
- Note: therapeutic drug level monitoring is recommended for itraconazole
- Source: IDSA guidelines 2007
Prevention
Lab Safety
- Biosafety risk group 3 organism, so needs BSL 3
- Should be suspected with any white mold
Prophylaxis
- May be indicated for endemic areas in patients with advanced HIV and low CD4 count