Gut microbiota: Difference between revisions
From IDWiki
Content deleted Content added
Created page with "==Background== * The gastrointestinal tract is normally colonized with a number of microbes * Comprised of an estimated 35,000 bacterial species * Bacteria are generally either in the phyla Bacteroidetes or Firmicutes * The gut flora are impacted by: ** Mode of delivery at birth (Cesarean section versus vaginal delivery) ** Diet during infancy (breast milk versus formula) ** Diet during adulthood (plant-based or meat-based) ** Use of antimicrobials * May play a r..." |
added picture |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
* The gastrointestinal tract is normally colonized with a number of microbes |
* The gastrointestinal tract is normally colonized with a number of microbes |
||
* Comprised of an estimated 35,000 bacterial species |
* Comprised of an estimated 35,000 bacterial species |
||
* Bacteria are generally either in the phyla [[Bacteroidetes]] or [[Firmicutes]] |
|||
* The gut flora are impacted by: |
* The gut flora are impacted by: |
||
** Mode of delivery at birth (Cesarean section versus vaginal delivery) |
** Mode of delivery at birth (Cesarean section versus vaginal delivery) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 8: | ||
** Use of antimicrobials |
** Use of antimicrobials |
||
* May play a role in a number of diseases |
* May play a role in a number of diseases |
||
== Members == |
|||
[[File:Gastrointestinal flora.jpg|alt=Gut microbial strains and negative health outcomes of gut microbial dysbiosis|thumb|Gut microbial strains and negative health outcomes of gut microbial dysbiosis. From: Afzaal et al. Human gut microbiota in health and disease: Unveiling the relationship. Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 26;13:999001. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.999001. PMID: 36225386; PMCID: PMC9549250.]] |
|||
* A healthy gut microbiota is dominated by bacteria in the phyla [[Bacteroidetes]] or [[Firmicutes]], followed by [[Actinobacteria]] and [[Verrucomicrobia]] |
|||
* Varies by location |
|||
** Esophagus: [[Bacteroides]], [[Gemella]], [[Megasphaera]], [[Pseudomonas]], [[Prevotella]], [[Rothia]], [[Streptococcus]], [[Veillonella]] |
|||
** Stomach: [[Streptococcus]], [[Lactobacillus]], [[Prevotella]], [[Enterococcus]], [[Helicobacter pylori]] |
|||
** Small intestine: [[Bacteroides]], [[Clostridium]], [[Streptococcus]], [[Lactobacillus]], [[Proteobacteria]], [[Enterococcus]] |
|||
** Cecum: [[Lachnospira]], [[Roseburia]], [[Butyrivibrio]], [[Ruminococcus]], [[Fecalibacterium]], [[Fusobacterium]] |
|||
** Colon: [[Bacteroides]], [[Clostridium]], [[Prevotella]], [[Porphyromonas]], [[Eubacterium]], [[Ruminococcus]], [[Streptococcus]], [[Enterobacterium]], [[Enterococcus]], [[Lactobacillus]], [[Peptostreptococcus]], [[Fusobacterium]] |
|||
== Further Reading == |
|||
* Role of the normal gut microbiota. ''World J Gastroenterol''. 2015;21(29):8787-803. doi: [https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i29.8787 10.3748/wjg.v21.i29.8787]. PMID: [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26269668 26269668]; PMCID: [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4528021/ PMC4528021]. |
|||
Latest revision as of 18:05, 19 June 2023
Background
- The gastrointestinal tract is normally colonized with a number of microbes
- Comprised of an estimated 35,000 bacterial species
- The gut flora are impacted by:
- Mode of delivery at birth (Cesarean section versus vaginal delivery)
- Diet during infancy (breast milk versus formula)
- Diet during adulthood (plant-based or meat-based)
- Use of antimicrobials
- May play a role in a number of diseases
Members
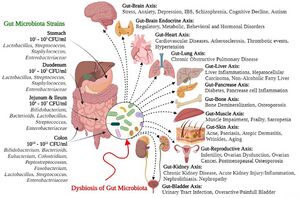
- A healthy gut microbiota is dominated by bacteria in the phyla Bacteroidetes or Firmicutes, followed by Actinobacteria and Verrucomicrobia
- Varies by location
- Esophagus: Bacteroides, Gemella, Megasphaera, Pseudomonas, Prevotella, Rothia, Streptococcus, Veillonella
- Stomach: Streptococcus, Lactobacillus, Prevotella, Enterococcus, Helicobacter pylori
- Small intestine: Bacteroides, Clostridium, Streptococcus, Lactobacillus, Proteobacteria, Enterococcus
- Cecum: Lachnospira, Roseburia, Butyrivibrio, Ruminococcus, Fecalibacterium, Fusobacterium
- Colon: Bacteroides, Clostridium, Prevotella, Porphyromonas, Eubacterium, Ruminococcus, Streptococcus, Enterobacterium, Enterococcus, Lactobacillus, Peptostreptococcus, Fusobacterium
Further Reading
- Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(29):8787-803. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i29.8787. PMID: 26269668; PMCID: PMC4528021.