Helicobacter pylori
From IDWiki
Helicobacter pylori
Background
- Slow-growing Gram-negative microaerophilic bacillus with a curve, gull-wing, or spiral appearance
- Oxidase-positive and urease-positive
- Major cause of peptic ulcer disease and gastric cancer worldwide
Pathophysiology
- Urease neutrolizes acid and induces angiogenesis
- Strains with CagA, VacA, and BabA are associated with more cellular metaplasia
Epidemiology
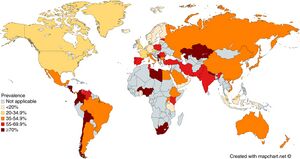
- Present worldwide
- About half of the world's population is estimated to have chronic infection1
- Usually acquired during infancy or childhood
- Transmission is likely fecal-oral or oral-oral
Clinical Manifestations
- Mostly asymptomatic
- Complications include:
- Peptic ulcer disease in 1 to 10%
- Gastric cancer in 0.1 to 3%
- MALT lymphoma in 0.01%
Diagnosis
- Gastroscopy with biopsy for histopathology is the gold standard
- Culture is challenging but necessary for phenotyping susceptibility testing
Urea Breath Test
- Patient is fed urea labelled with 13C or 14C isotopes, which is hydrolyzed into ammonia and isotope-labelled CO2, which is detected in exhaled breath 30 minutes later and measured by mass spectrometry (or other method)
- The delta over baseline (DOB) (i.e. increase in labelled CO2) is compared to a threshold
- Cutoff DOB is usually 5%
- False negatives may be seen with PPIs (which should be held for 7 days before test), recent antibiotics (should be off of them for 4 weeks before test), bleeding ulcers (should be resolved before test), and corpus-predominant gastritis
- False positives may be seen with Helicobacter heilmannii and rarely with other urease-producing organisms such as Proteus mirabilis, Citrobacter freundii, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus capitis subsp. urealyticus
Stool Antigen Test
- Non-invasive testing, and preferred to pediatric patients
- Based on ELISA, immunochromatographic assay, and CLIA
- Affected by PPIs (should be held for 7-14 days)2, antibiotics, bismuth-containing medications, and N-acetylcysteine
- Sample is temperature sensitive: max 24 hours at room temperature, 72 hours at 4ºC, or long-term if frozen
Serology
- Includes IgM, IgA, and IgG antibodies
- More false positives with IgA and IgM
- Post-treatment IgG titres can take 6-12 months to fall below 50% compared to pre-treatment
- Not affected by concurrent medications, unlike other non-invasive tests
- Accuracy varies by strain, so ideally should use locally-validated tests
Test of Cure
- Urea breath test is preferred to stool antigen
- Serology not helpful
Management
- Treatment is with combination therapy for 14 days followed by confirmation of eradication
- First-line:
- PBMT (BMT Quad): bismuth subsalicylate 524 mg p.o. four time daily, metronidazole 500 mg p.o. three to four times daily, tetracycline 500 mg p.o. four times daily for 14 days
- PAMC (CLAMET Quad): PPI twice daily, amoxicillin 1 g p.o. twice daily, metronidazole 500 mg p.o. twice daily, and clarithromycin 500 mg p.o. twice daily for 14 days
- PAC (PPI, amoxicillin, clarithromycin), PMC (PPI, metronidazole, clarithromycin), or PAM (PPI, amoxicillin, metronidazole) only in areas with clarithromycin resistance <15% or with proven high local eradication rates >85%
- Prior treatment failure:
- PBMT: PPI twice daily, bismuth subsalicylate 524 mg p.o. four times daily, metronidazole 500 mg p.o. three to four times daily, tetracycline 500 mg p.o. four times daily
- PAL: PPI twice daily, levofloxacin 500 mg p.o. once daily, and amoxicillin 750 mg p.o. three times daily for 14 days
- PAR: PPI twice daily, amoxicillin 750 mg p.o. three times daily, and rifabutin 300 mg p.o. once daily for 10-14 days
- Duration generally 14 days
- Confirmation of eradication should be done 4 weeks following treatment
- Recommended order of treatment, if persistently positive:
Antibiotic Resistance
- Mechanisms:
- Amoxicillin resistance is caused by modified PBPs (rather than β-lactamases)
- Clarithromycin resistance is caused by point mutations in the 23S rRNA of 50S ribosomal subunit
- Metronidazole resistance is caused by mutations in RdxA and FrxA enzymes
- Levofloxacin resistance is caused by point mutations in DNA gyrase (gyrA or gyrB)
- Tetracycline resistance is uncommon and not fully understood
- Rifabutin resistance is uncommon and caused by mutations in DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
- The most important regional rates of resistance to pay attention to when choosing empiric treatment is to clarithromycin and metronidazole, since they are most frequent
Further Reading
- H. pylori Enhanced Primary Care Pathway: 2016 version, 2019 version, 2020 version
- The Toronto Consensus for the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Adults. Gastroenterol. 2016;151:51–69. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.04.006
- Houston Consensus Conference on Testing for Helicobacter pylori Infection in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(7):992-1002.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.03.013
References
- ^ M. Zamani, F. Ebrahimtabar, V. Zamani, W. H. Miller, R. Alizadeh‐Navaei, J. Shokri‐Shirvani, M. H. Derakhshan. Systematic review with meta‐analysis: the worldwide prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 2018;47(7):868-876. doi:10.1111/apt.14561.
- ^ G. Manes, A. Balzano, G. Iaquinto, C. Ricci, M. M. Piccirillo, N. Giardullo, A. Todisco, M. Lioniello, D. Vaira. Accuracy of the stool antigen test in the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection before treatment and in patients on omeprazole therapy. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 2001;15(1):73-79. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2036.2001.00907.x.