Helicobacter pylori: Difference between revisions
From IDWiki
Helicobacter pylori
m (ββ) |
No edit summary Β |
||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
*Treatment is with combination therapy for 14 days followed by confirmation of eradication |
*Treatment is with combination therapy for 14 days followed by confirmation of eradication |
||
*First-line: |
*First-line: |
||
| β | **[[PBMT]] ( |
+ | **[[PBMT]] (BMT Quad): bismuth subsalicylate 524 mg p.o. four time daily, metronidazole 500 mg p.o. three to four times daily, tetracycline 500 mg p.o. four times daily for 14 days |
| β | **[[PAMC]] (PPI, [[amoxicillin]], |
+ | **[[PAMC]] (CLAMET Quad): PPI twice daily, [[amoxicillin]] 1 g p.o. twice daily, metronidazole 500 mg p.o. twice daily, and [[clarithromycin]] 500 mg p.o. twice daily for 14 days |
**[[PAC]] (PPI, [[amoxicillin]], [[clarithromycin]]), PMC (PPI, [[metronidazole]], [[clarithromycin]]), or [[PAM]] (PPI, [[amoxicillin]], [[metronidazole]]) only in areas with [[clarithromycin]] resistance <15% or with proven high local eradication rates >85% |
**[[PAC]] (PPI, [[amoxicillin]], [[clarithromycin]]), PMC (PPI, [[metronidazole]], [[clarithromycin]]), or [[PAM]] (PPI, [[amoxicillin]], [[metronidazole]]) only in areas with [[clarithromycin]] resistance <15% or with proven high local eradication rates >85% |
||
*Prior treatment failure: |
*Prior treatment failure: |
||
| β | **[[PBMT]] |
+ | **[[PBMT]]: PPI twice daily, bismuth subsalicylate 524 mg p.o. four times daily, [[metronidazole]] 500 mg p.o. three to four times daily, [[tetracycline]] 500 mg p.o. four times daily |
| + | **[[PAL]]: PPI twice daily, [[levofloxacin]] 500 mg p.o. once daily, and [[amoxicillin]] 750 mg p.o. three times daily for 14 days |
||
| β | **[[PAL]] (PPI, [[amoxicillin]], [[levofloxacin]]) |
||
| β | **[[PAR]] |
+ | **[[PAR]]: PPI twice daily, amoxicillin 750 mg p.o. three times daily, and rifabutin 300 mg p.o. once daily for 10-14 days |
| ⚫ | |||
| β | *Doses: |
||
| β | **[[PBMT]] |
||
| β | ***Bismuth subsalicylate 524 mg (2x 262 mg tablets) PO qid |
||
| β | ***[[Metronidazole]] 500 mg PO tid or qid |
||
| β | ***PPI: [[esomeprazole]] 20 mg, [[lansoprazole]] 30 mg, [[omeprazole]] 20 mg, [[pantoprazole]] 40 mg, or [[rabeprazole]] 20 mg |
||
| β | ****Some areas use double dosing |
||
| β | ***[[Tetracycline]] 500 mg PO qid |
||
| β | **Others |
||
| β | ***[[Amoxicillin]] 1000 mg PO bid |
||
| β | ***[[Clarithromycin]] 500 mg PO bid |
||
| β | ***[[Levofloxacin]] 500 mg PO daily |
||
| β | ***[[Metronidazole]] 500 mg PO bid |
||
| β | ***[[Rifabutin]] 150 mg PO bid |
||
| β | ***PPI as above |
||
| ⚫ | |||
*Confirmation of eradication should be done 4 weeks following treatment |
*Confirmation of eradication should be done 4 weeks following treatment |
||
*Recommended order of treatment, if persistently positive: |
*Recommended order of treatment, if persistently positive: |
||
| Line 100: | Line 86: | ||
** [[Levofloxacin]] resistance is caused by point mutations in DNA gyrase (''gyrA'' or ''gyrB'') |
** [[Levofloxacin]] resistance is caused by point mutations in DNA gyrase (''gyrA'' or ''gyrB'') |
||
** [[Tetracycline]] resistance is uncommon and not fully understood |
** [[Tetracycline]] resistance is uncommon and not fully understood |
||
| β | ** [[Rifabutin]] resistance is uncommon caused by mutations in DNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
+ | ** [[Rifabutin]] resistance is uncommon and caused by mutations in DNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
* The most important regional rates of resistance to pay attention to when choosing empiric treatment is to [[clarithromycin]] and [[metronidazole]], since they are most frequent |
* The most important regional rates of resistance to pay attention to when choosing empiric treatment is to [[clarithromycin]] and [[metronidazole]], since they are most frequent |
||
Latest revision as of 10:44, 2 May 2024
Background
- Slow-growing Gram-negative microaerophilic bacillus with a curve, gull-wing, or spiral appearance
- Oxidase-positive and urease-positive
- Major cause of peptic ulcer disease and gastric cancer worldwide
Pathophysiology
- Urease neutrolizes acid and induces angiogenesis
- Strains with CagA, VacA, and BabA are associated with more cellular metaplasia
Epidemiology
- Present worldwide
- About half of the world's population is estimated to have chronic infection[1]
- Usually acquired during infancy or childhood
- Transmission is likely fecal-oral or oral-oral
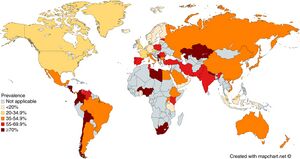
Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection across the world. From: Zamani et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the worldwide prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018;47(7):868-876. doi: 10.1111/apt.14561.
Clinical Manifestations
- Mostly asymptomatic
- Complications include:
- Peptic ulcer disease in 1 to 10%
- Gastric cancer in 0.1 to 3%
- MALT lymphoma in 0.01%
Diagnosis
- Gastroscopy with biopsy for histopathology is the gold standard
- Culture is challenging but necessary for phenotyping susceptibility testing
Urea Breath Test
- Patient is fed urea labelled with 13C or 14C isotopes, which is hydrolyzed into ammonia and isotope-labelled CO2, which is detected in exhaled breath 30 minutes later and measured by mass spectrometry (or other method)
- The delta over baseline (DOB) (i.e. increase in labelled CO2) is compared to a threshold
- Cutoff DOB is usually 5%
- False negatives may be seen with PPIs (which should be held for 7 days before test), recent antibiotics (should be off of them for 4 weeks before test), bleeding ulcers (should be resolved before test), and corpus-predominant gastritis
- False positives may be seen with Helicobacter heilmannii and rarely with other urease-producing organisms such as Proteus mirabilis, Citrobacter freundii, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus capitis subsp. urealyticus
Stool Antigen Test
- Non-invasive testing, and preferred to pediatric patients
- Based on ELISA, immunochromatographic assay, and CLIA
- Affected by PPIs (should be held for 7-14 days)[2], antibiotics, bismuth-containing medications, and N-acetylcysteine
- Sample is temperature sensitive: max 24 hours at room temperature, 72 hours at 4ΒΊC, or long-term if frozen
Serology
- Includes IgM, IgA, and IgG antibodies
- More false positives with IgA and IgM
- Post-treatment IgG titres can take 6-12 months to fall below 50% compared to pre-treatment
- Not affected by concurrent medications, unlike other non-invasive tests
- Accuracy varies by strain, so ideally should use locally-validated tests
Test of Cure
- Urea breath test is preferred to stool antigen
- Serology not helpful
Management
- Treatment is with combination therapy for 14 days followed by confirmation of eradication
- First-line:
- PBMT (BMT Quad): bismuth subsalicylate 524 mg p.o. four time daily, metronidazole 500 mg p.o. three to four times daily, tetracycline 500 mg p.o. four times daily for 14 days
- PAMC (CLAMET Quad): PPI twice daily, amoxicillin 1 g p.o. twice daily, metronidazole 500 mg p.o. twice daily, and clarithromycin 500 mg p.o. twice daily for 14 days
- PAC (PPI, amoxicillin, clarithromycin), PMC (PPI, metronidazole, clarithromycin), or PAM (PPI, amoxicillin, metronidazole) only in areas with clarithromycin resistance <15% or with proven high local eradication rates >85%
- Prior treatment failure:
- PBMT: PPI twice daily, bismuth subsalicylate 524 mg p.o. four times daily, metronidazole 500 mg p.o. three to four times daily, tetracycline 500 mg p.o. four times daily
- PAL: PPI twice daily, levofloxacin 500 mg p.o. once daily, and amoxicillin 750 mg p.o. three times daily for 14 days
- PAR: PPI twice daily, amoxicillin 750 mg p.o. three times daily, and rifabutin 300 mg p.o. once daily for 10-14 days
- Duration generally 14 days
- Confirmation of eradication should be done 4 weeks following treatment
- Recommended order of treatment, if persistently positive:
Antibiotic Resistance
- Mechanisms:
- Amoxicillin resistance is caused by modified PBPs (rather than Ξ²-lactamases)
- Clarithromycin resistance is caused by point mutations in the 23S rRNA of 50S ribosomal subunit
- Metronidazole resistance is caused by mutations in RdxA and FrxA enzymes
- Levofloxacin resistance is caused by point mutations in DNA gyrase (gyrA or gyrB)
- Tetracycline resistance is uncommon and not fully understood
- Rifabutin resistance is uncommon and caused by mutations in DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
- The most important regional rates of resistance to pay attention to when choosing empiric treatment is to clarithromycin and metronidazole, since they are most frequent
Further Reading
- H. pylori Enhanced Primary Care Pathway: 2016 version, 2019 version, 2020 version
- The Toronto Consensus for the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Adults. Gastroenterol. 2016;151:51β69. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.04.006
- Houston Consensus Conference on Testing for Helicobacter pylori Infection in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(7):992-1002.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.03.013
- β Zamani M, Ebrahimtabar F, Zamani V, Miller WH, Alizadeh-Navaei R, Shokri-Shirvani J, Derakhshan MH. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the worldwide prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Apr;47(7):868-876. doi: 10.1111/apt.14561. Epub 2018 Feb 12. PMID: 29430669.
- β Manes G, Balzano A, Iaquinto G, Ricci C, Piccirillo MM, Giardullo N, Todisco A, Lioniello M, Vaira D. Accuracy of the stool antigen test in the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection before treatment and in patients on omeprazole therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001 Jan;15(1):73-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.2001.00907.x. PMID: 11136280.