Aminoglycosides: Difference between revisions
From IDWiki
Content deleted Content added
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<br /> |
<br /> |
||
== |
==Background== |
||
*Derived from [[Streptomyces species]] (mycins & kacins) or [[Micromonospora species]] (micins) |
*Derived from [[Streptomyces species]] (mycins & kacins) or [[Micromonospora species]] (micins) |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
===Traditional Dosing=== |
===Traditional Dosing=== |
||
*Used for Enterococcus IE, meningitis, septic shock, ascites, AKI/CKD, |
*Used for Enterococcus IE, meningitis, septic shock, ascites, AKI/CKD, pregnancy, surgical prophylaxis, burns, osteomyelitis |
||
*1.7mg/kg (5-7.5mg/kg amikacin) |
*1.7mg/kg (5-7.5mg/kg amikacin) |
||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
*1mg/kg divided q8-12h, peak target 3-5, trough <2 |
*1mg/kg divided q8-12h, peak target 3-5, trough <2 |
||
=== |
===Monitoring=== |
||
====Peak==== |
====Peak==== |
||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
[[File:Hartford_nomogram.png]] |
[[File:Hartford_nomogram.png]] |
||
* |
*Double the concentration for [[amikacin]] |
||
== |
==Safety== |
||
===Adverse Drug Reactions=== |
===Adverse Drug Reactions=== |
||
Revision as of 19:21, 18 September 2020
Background
- Derived from Streptomyces species (mycins & kacins) or Micromonospora species (micins)
Mechanism of Action
- Requires electron transport chain (ETC) to cross over the membrane
- Anaerobes are therefore inherently resistant
- Reversibly binds 30S ribosomal subunit, which stops proofreading and causes accumulation of bad proteins
Spectrum of Activity
- Good coverage of Gram-negative aerobes
- Except Stenotrophomonas and Burkholderia
- Streptomycin also covers mycobacterium
- Some protozoal coverage
- Can cover Gram-positives if cell wall is disrupted (e.g. by beta-lactam)
Mechanisms of Resistance
- Altered 50S ribosomal subunit
- Decreased uptake and accumulation (Pseudomonas)
- Decreased membrane permeability
- Efflux (E. coli)
- Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes (Enterococcus)
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
- Poor membrane penetration, therefore doesn't cross over into lungs and CSF
- Half-life 2-3 hours (longer in CKD)
- Excreted 99% unchanged in urine
- Displays concentration-depedent killing with a prolonged post-antibiotic effect (2-13 hours)
Dosing
Initial Dose
If actual body weight more than 20% higher than ideal body weight, need to calculate adjusted body weight (ABW)
$$ABW = IBW + 0.4 \times (actual BW - IBW)$$
Traditional Dosing
- Used for Enterococcus IE, meningitis, septic shock, ascites, AKI/CKD, pregnancy, surgical prophylaxis, burns, osteomyelitis
- 1.7mg/kg (5-7.5mg/kg amikacin)
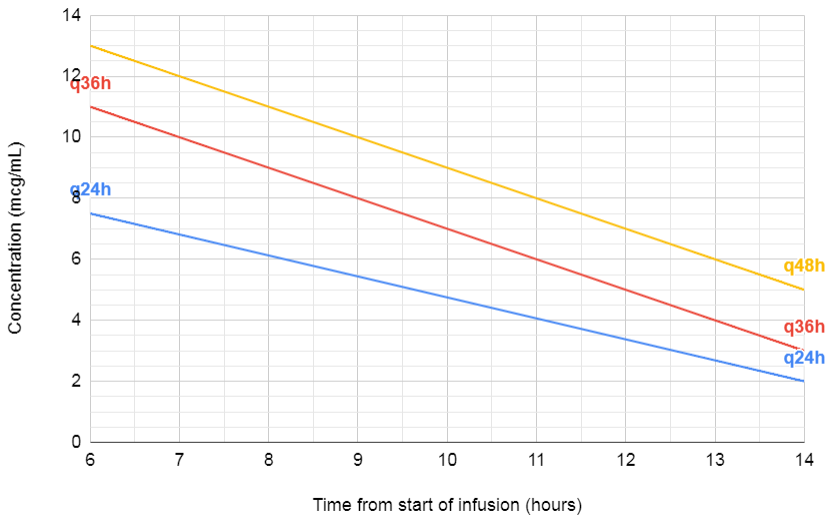
Extended Interval Dosing
- 7mg/kg (15mg/kg amikacin)
- Use Hartford nomogram with a random level (but remember to halve the amikacin level first)
- CrCl ≥60 q24h
- CrCl 40-59 q36h
- CrCl 20-39 q48h
- CrCl ≤19 don't use
Dialysis Dosing
- Pre-HD levels with post-HD doses, though this may change
Synergy
- 1mg/kg divided q8-12h, peak target 3-5, trough <2
Monitoring
Peak
- 30min after third dose
- Response is based on peak:MIC ratio, target is 8-10 times
- If below target, increase dose
Trough
- Prior to 4th dose, or a random level at 24-48h in renal failure
- Side effects are predicted by trough levels
- Tobra <0.5 (extended) or <2 (traditional)
- Amikacin <1 (extended) or <?? (traditional)
- If above target, increase interval
Hartford Nomogram
- Double the concentration for amikacin
Safety
Adverse Drug Reactions
- Nephrotoxicity (0-50%), usually non-oliguric AKI with decreased Ca/Mg resorption, often reversible
- Decreased protein synthesis
- Decreased cellular respiration
- Increased apoptosis
- Necrosis in proximal tubules
- Ototoxicity (0-60%), irreversible
- Cumulative effect
- Distribute into the perilymph of the ear, and cause free radical formation causing apoptosis of hair cells
- Needs hearing tests, because it can be subclinical
- Monitor audiometry weekly
- Vestibulotoxicity (0-20%), irreversible
- Rarely, neuromuscular blockade
Monitoring
- Trough levels
- Creatinine
- Weekly audiometry